Clinical Example: Radical flexor synovectomy hand and forearm for granulomatous synovitis
| Flexor synovitis occasionally is due to fungal or mycobacterial infection, producing a granulomatous reaction. These present as a slowly progressive process, worsening over months. There may be a history of a finger puncture injury preceeding symptoms. There is typically less local tenderness than would be expected for the degree of swelling, stiffness and pain. Local steroid injections are ineffective and may be followed by rapid clinical worsening. Cure requires thorough synovectomy and culture directed antibiotic treatment. |
| Click on each image for a larger picture |
| This man presented with a
one year history of progressively worsening right hand pain, swelling
and loss of flexion. Symptoms began one month after a right
ring finger puncture wound in a marine setting. He had been given a
trigger finger steroid injection months earlier with no relief. |
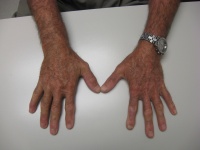
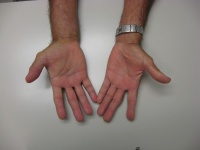
| The right palm and forearm
were full, but not tender. Fingtips could only be brought to
within 2" of the distal palmar crease. No fever, no
lymphadenopathy. Rheumatologic tests including sedimentation rate were
normal. |
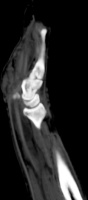
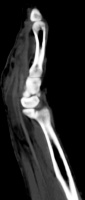
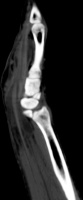
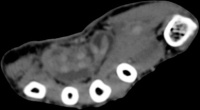
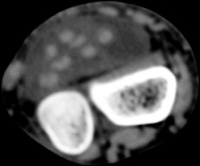
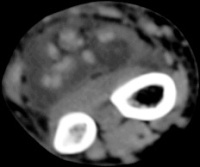
| The radiologist
interpreted his MRI as normal, but these views show bulky, edematous
flexor synovitis. |

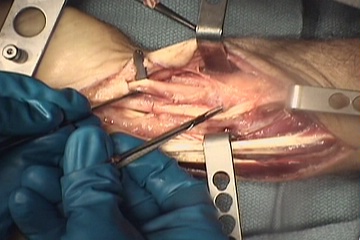
| A radical flexor
tenosynovectomy was performed for the presumed diagnosis of synovitis
from atypical infection. The initial extensile here is
planned from the mid palm to the mid forearm. |
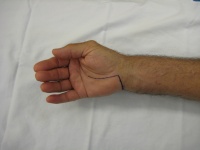
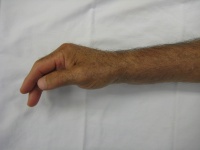
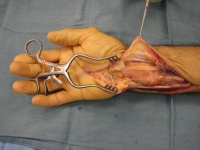
| Bulky, edematous synovitis
involved all flexor tendons. |

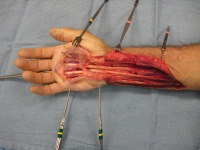
| Palmar exposure was
extended to include a distal "Y" shaped incision. Here, the synovecomy
is complete. |
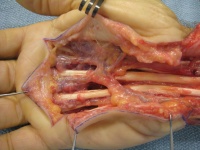
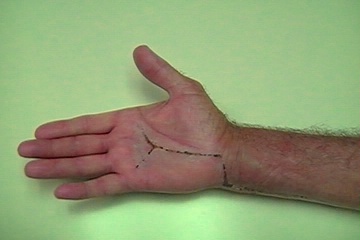
| Closure. |
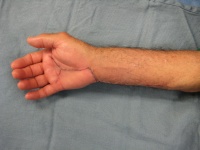
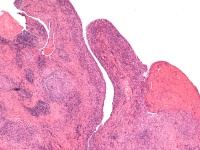
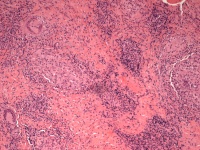
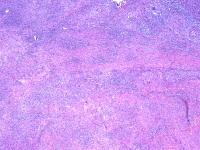
| Histology confirmed
granulomatous synovitis. Unfortunately, no organisms were identified,
even in long term culture for fungus and mycobacteria. This confirms
the need for complete synovectomy. |

| Videos |
||
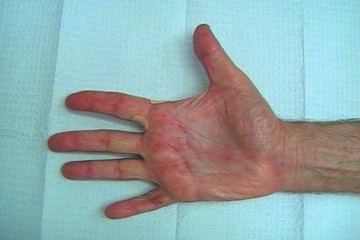
| Step by Step Surgery | 2 Weeks Postop | 6 Weeks Postop |
 |
 |
 |
| Search
for... atypical mycobacterium hand granulomatous synovitis hand |
Case Examples Index Page | e-Hand home |